If you are interested to learn about the react table
A map is a data collection type where data is stored in the form of pairs. It contains a unique key. The value stored in the map must be mapped to the key. We cannot store a duplicate pair in the map(). It is because of the uniqueness of each stored key. It is mainly used for fast searching and looking up data.
The map() function is used to iterate over an array and manipulate or change data items. In React, the map() function is most commonly used for rendering a list of data to the DOM.
In React, the ?map? method used to traverse and display a list of similar objects of a component. A map is not the feature of React. Instead, it is the standard JavaScript function that could be called on any array. The map() method creates a new array by calling a provided function on every element in the calling array.
Example
In the given example, the map() function takes an array of numbers and double their values. We assign the new array returned by map() to the variable doubleValue and log it.
var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const doubleValue = numbers.map((number)=>{
return (number * 2);
});
console.log(doubleValue); How to use map function
Add a new file in src folder and named it as Mapdemo.js as below.

import React,{Component } from 'react'
function MapDemo(){
const array1 = [1,2,3,4,5];
const map1 = array1.map(item => item*2 + ",")
return(
<h3>{map1}</h3>
)
}
export default MapDemo;Go to App.js and import this component and use it.

Description of code
Here we have taken a simple array ayyar1 of number and we want to transform an array of multiply by 2 using this array. So, for applying this transformation, map takes the function which we pass as an argument and that function will get executed for every item in a given array. The result of this function will be stored in newly created array.
Use “npm start” to run the project in localhost.

n React, the map() method used for:
1. Traversing the list element.
Example
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
function NameList(props) {
const myLists = props.myLists;
const listItems = myLists.map((myList) =>
<li>{myList}</li>
);
return (
<div>
<h2>React Map Example</h2>
<ul>{listItems}</ul>
</div>
);
}
const myLists = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'D'];
ReactDOM.render(
<NameList myLists={myLists} />,
document.getElementById('app')
);
export default App; Output
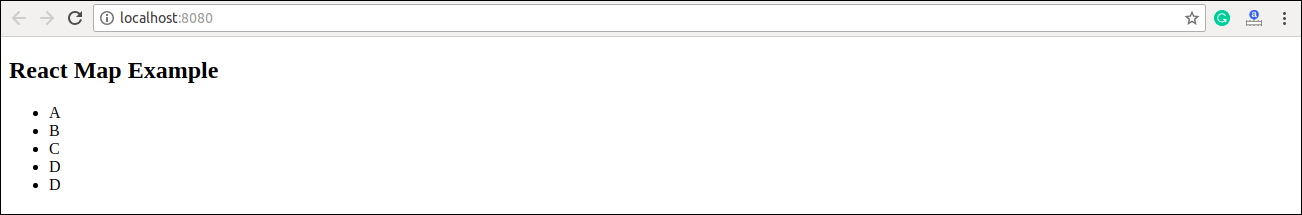
2. Traversing the list element with keys.
Example
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
function ListItem(props) {
return <li>{props.value}</li>;
}
function NumberList(props) {
const numbers = props.numbers;
const listItems = numbers.map((number) =>
<ListItem key={number.toString()}
value={number} />
);
return (
<div>
<h2>React Map Example</h2>
<ul> {listItems} </ul>
</div>
);
}
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
ReactDOM.render(
<NumberList numbers={numbers} />,
document.getElementById('app')
);
export default App; Output
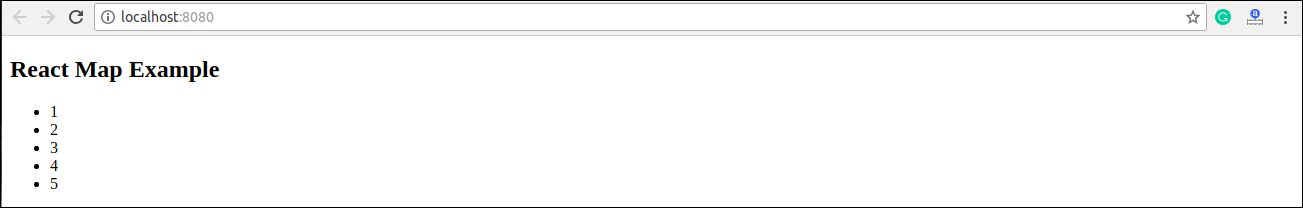
Conclusion
Using the map() function, you can pretty much do all sorts of manipulations without mutating the original array. The non-mutation part is essential, as it does not cause any side effects by default and makes it easy to debug your code. If you want to mutate the original array, you can use the traditional for or any other type of loop, or you can use the forEach() function.


