What is the MySQL DELETE Statement?
The DELETE statement is used to delete existing records in a table. MySQL DELETE statement is used to remove records from the MySQL table that is no longer required in the database. This query in MySQL deletes a full row from the table and produces the count of deleted rows. It also allows us to delete more than one record from the table within a single query, which is beneficial while removing large numbers of records from a table. By using the delete statement, we can also remove data based on conditions.
Once we delete the records using this query, we cannot recover it. Therefore before deleting any records from the table, it is recommended to create a backup of your database. The database backups allow us to restore the data whenever we need it in the future.
DELETE Syntax
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;Note: Be careful when deleting records in a table! Notice the WHERE clause in the DELETE statement. The WHERE clause specifies which record(s) should be deleted. If you omit the WHERE clause, all records in the table will be deleted!
How do I write a delete statement in MySQL?
To delete rows in a MySQL table, use the DELETE FROM statement: DELETE FROM products WHERE product_id=1; The WHERE clause is optional, but you’ll usually want it, unless you really want to delete every row from the table.
How do I delete a record in MySQL?
MySQL DELETE Statement
- DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;
- Example. DELETE; FROM ;Customers; WHERE CustomerName=’Alfreds Futterkiste’;
- DELETE FROM table_name;
- Example. DELETE; FROM; Customers;
Demo Database
Below is a selection from the “Customers” table in the Northwind sample database:
| CustomerID | CustomerName | ContactName | Address | City | PostalCode | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alfreds Futterkiste | Maria Anders | Obere Str. 57 | Berlin | 12209 | Germany |
| 2 | Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados | Ana Trujillo | Avda. de la Constitución 2222 | México D.F. | 05021 | Mexico |
| 3 | Antonio Moreno Taquería | Antonio Moreno | Mataderos 2312 | México D.F. | 05023 | Mexico |
| 4 | Around the Horn | Thomas Hardy | 120 Hanover Sq. | London | WA1 1DP | UK |
| 5 | Berglunds snabbköp | Christina Berglund | Berguvsvägen 8 | Luleå | S-958 22 | Sweden |
SQL DELETE Example
The following SQL statement deletes the customer “Alfreds Futterkiste” from the “Customers” table:
Example
DELETE ;FROM ;Customers ;WHERE ;CustomerName='Alfreds Futterkiste';
The “Customers” table will now look like this:
| CustomerID | CustomerName | ContactName | Address | City | PostalCode | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados | Ana Trujillo | Avda. de la Constitución 2222 | México D.F. | 05021 | Mexico |
| 3 | Antonio Moreno Taquería | Antonio Moreno | Mataderos 2312 | México D.F. | 05023 | Mexico |
| 4 | Around the Horn | Thomas Hardy | 120 Hanover Sq. | London | WA1 1DP | UK |
| 5 | Berglunds snabbköp | Christina Berglund | Berguvsvägen 8 | Luleå | S-958 22 | Sweden |
Delete All Records
It is possible to delete all rows in a table without deleting the table. This means that the table structure, attributes, and indexes will be intact:DELETE FROM table_name; The following SQL statement deletes all rows in the “Customers” table, without deleting the table:
Example
DELETE ;FROM ;Customers;
More Examples
Here, we are going to use the “Employees” and “Payment” tables for the demonstration of the DELETE statement. Suppose the Employees and Payment tables contain the following data:
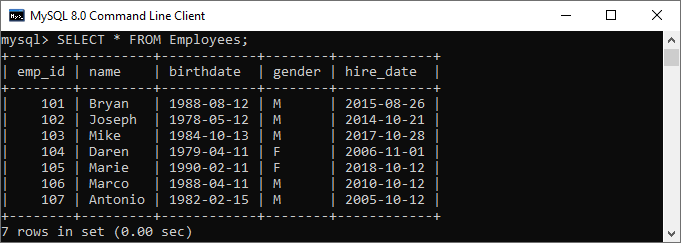
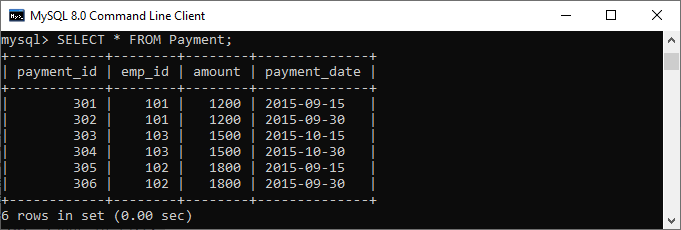
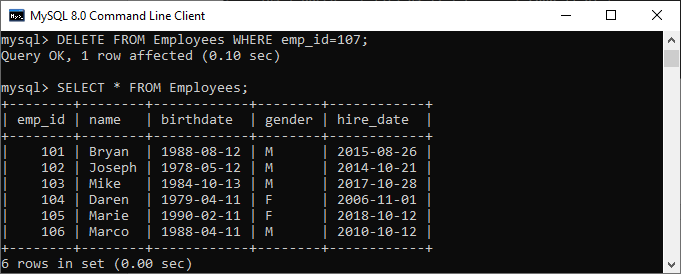
If we want to delete an employee whose emp_id is 107, we should use the DELETE statement with the WHERE clause. See the below query:
mysql> <strong>DELETE</strong> <strong>FROM</strong> Employees <strong>WHERE</strong> emp_id=107;
After the execution of the query, it will return the output as below image. Once the record is deleted, verify the table using the SELECT statement:
If we want to delete all records from the table, there is no need to use the WHERE clause with the DELETE statement.
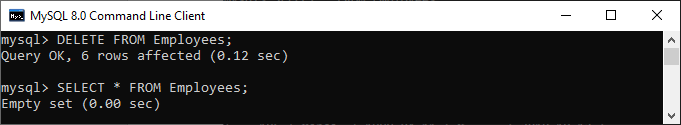
In the above output, we can see that after removing all rows, the Employees table will be empty. It means no records available in the selected table.
MySQL DELETE and LIMIT Clause
MySQL Limit clause is used to restrict the count of rows returns from the result set, rather than fetching the whole records in the table. Sometimes we want to limit the number of rows to be deleted from the table; in that case, we will use the LIMITclause as follows:
- DELETE FROM table_name
- WHERE condition
- ORDER BY colm1, colm2, …
- LIMIT row_count;
It is to note that the order of rows in a MySQL table is unspecified. Therefore, we should always use the ORDER BY clause while using the LIMIT clause.
For example, the following query first sorts the employees according to their names alphabetically and deletes the first three employees from the table:
mysql> <strong>DELETE</strong> <strong>FROM</strong> Employees <strong>ORDER</strong> <strong>BY</strong> <strong>name</strong> LIMIT 3;


