A loops causes a specific block of statements to be repeated a specific number of time as long as some condition remains true.
- While loop
- Do-while loop
- For loop
- For IN
JavaScript supports all the necessary loops to ease down the pressure of programming.
The while Loop
The most basic loop in JavaScript is the while loop which would be discussed in this chapter. The purpose of a while loop is to execute a statement or code block repeatedly as long as an expression is true. Once the expression becomes false, the loop terminates.
Flow Chart
The flow chart of while loop looks as follows:

Syntax
The syntax of while loop in JavaScript is as follows-
while (expression) {
Statement(s) to be executed
if expression is true
}Example
Try the following example to implement while loop.
<html>
<body>
<script type =
"text/javascript">
<!--
var count = 0;
document.write("Starting Loop
");
while (count < 10) {
document.write("Current Count :
" + count + "<br />");
count++;
}
document.write("Loop
stopped!");
//-->
</script>
<p>Set the variable to
different value and then
try...</p>
</body>
</html>Output
Starting Loop
Current Count : 0
Current Count : 1
Current Count : 2
Current Count : 3
Current Count : 4
Current Count : 5
Current Count : 6
Current Count : 7
Current Count : 8
Current Count : 9
Loop stopped!
Set the variable to different
value and then try...The do…while Loop
The do…while loop is similar to the while loop except that the condition check happens at the end of the loop. This
means that the loop will always be executed at least once, even if the condition is false.
Flow Chart
The flow chart of a do-while loop would be as follows

Syntax
The syntax for do-while loop in JavaScript is as follows −
do {
Statement(s) to be executed;
} while (expression);Note − Don’t miss the semicolon used at the end of the do…while loop.
Example
Try the following example to learn how to implement a do-while loop in JavaScript
<html>
<body>
<script type =
"text/javascript">
<!--
var count = 0;
document.write("Starting Loop" +
"<br />");
do {
document.write("Current Count :
" + count + "<br />");
count++;
}
while (count < 5);
document.write
("Loop stopped!");
//-->
</script>
<p>Set the variable to
different value and then
try...</p>
</body>
</html>Output
Starting Loop
Current Count : 0
Current Count : 1
Current Count : 2
Current Count : 3
Current Count : 4
Loop Stopped!
Set the variable to different value and then try…For loop
The ‘for’ loop is the most compact form of looping. It includes the following three important parts
- The loop initialization where we initialize our counter to a starting value. The initialization statement is execute before the loop begins
- The test statement which will test if a given condition is true or not. If the condition is true, then the code given inside the loop will be executed, otherwise the control will come out of the loop.
- The iteration statement where you can increase or decrease your counter.
You can put all the three parts in a single line separated by semicolons
Flow Chart
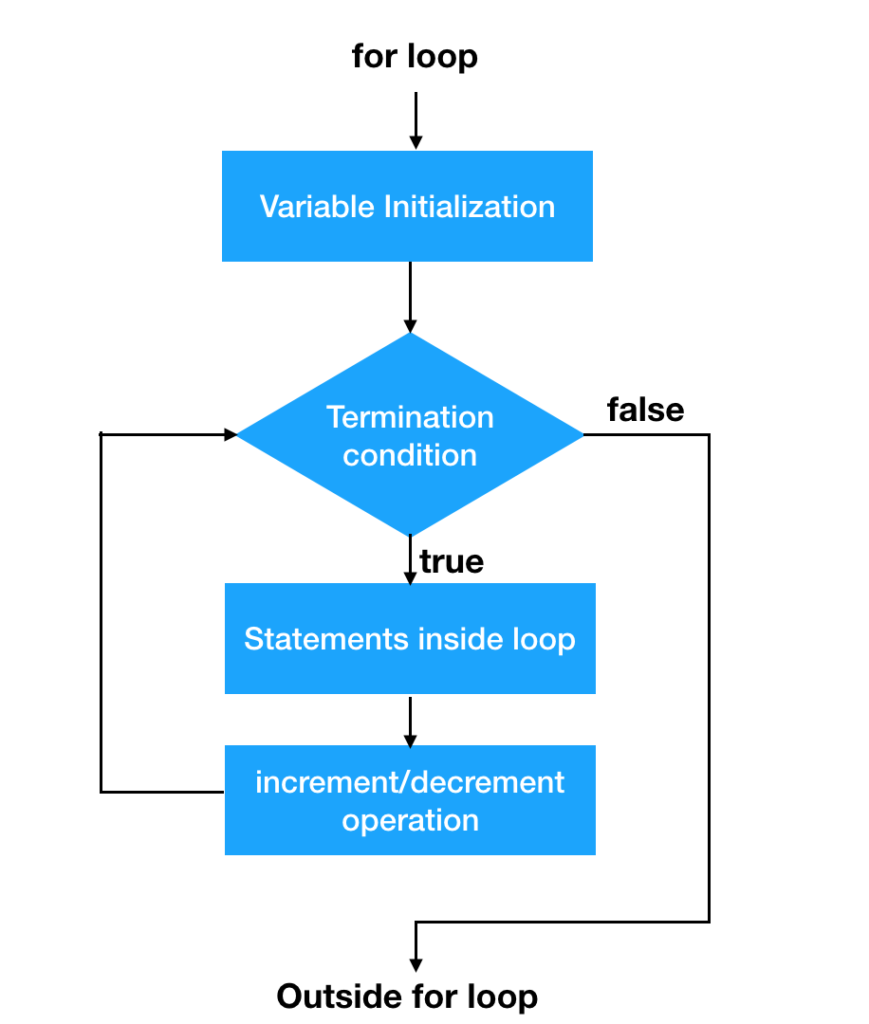
The flow chart of a for loop in JavaScript would be as follows
Syntax
The syntax of for loop is JavaScript is as follows −
for (initialization; test
condition; iteration statement)
{
Statement(s) to be executed
if test condition is true
}
Example
Try the following example to learn how a for loop works in JavaScript.
<html>
<body>
<script type =
"text/javascript">
<!--
var count;
document.write("Starting Loop" +
"<br />");
for(count = 0; count
< 10; count++) {
document.write("Current Count :
" + count );
document.write("<br />");
}
document.write("Loop
stopped!");
//-->
</script>
<p>Set the variable to
different value and then
try...</p>
</body>
</html>
Output
Starting Loop
Current Count : 0
Current Count : 1
Current Count : 2
Current Count : 3
Current Count : 4
Current Count : 5
Current Count : 6
Current Count : 7
Current Count : 8
Current Count : 9
Loop stopped!
Set the variable to different
value and then try…For in
The for…in loop is used to loop through an object’s properties. As we have not discussed Objects yet, you may not feel
comfortable with this loop. But once you understand how objects behave in JavaScript, you will find this loop very useful.
Syntax
The syntax of ‘for. In’ loop is −
for (variablename in object) {
statement or block to execute
}In each iteration, one property from object is assigned to variable name and this loop continues till all the properties of the object are exhausted.
Example
Try the following example to implement ‘for-in’ loop. It prints the web browser’s Navigator object.
<html>
<body>
<script type =
"text/javascript">
<!--
var aProperty;
document.write("Navigator Object
Properties<br /> ");
for (aProperty in
navigator) {
document.write(aProperty);
document.write("<br />");
}
document.write
("Exiting from the loop!");
//-->
</script>
<p>Set the variable to
different object and then
try...</p>
</body>
</html>Output
Navigator Object Properties
serviceWorker
webkitPersistentStorage
webkitTemporaryStorage
geolocation
doNotTrack
onLine
languages
language
userAgent
product
platform
appVersion
appName
appCodeName
hardwareConcurrency
maxTouchPoints
vendorSub
vendor
productSub
cookieEnabled
mimeTypes
plugins
javaEnabled
getStorageUpdates
getGamepads
webkitGetUserMedia
vibrate
getBattery
sendBeacon
registerProtocolHandler
unregisterProtocolHandler
Exiting from the loop!
Set the variable to different
object and then try...

