The temporary tables could be very useful in some cases to keep temporary data. The most important thing that should be known for temporary tables is that they will be deleted when the current client session terminates.
What are Temporary Tables?
Temporary tables were added in the MySQL Version 3.23. If you use an older version of MySQL than 3.23, you cannot use the temporary tables, but you can use Heap Tables.
As stated earlier, temporary tables will only last as long as the session is alive. If you run the code in a PHP script, the temporary table will be destroyed automatically when the script finishes executing. If you are connected to the MySQL database server through the MySQL client program, then the temporary table will exist until you close the client or manually destroy the table.
How does MySQL store temp data?
To create a temporary table, you must have the CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES privilege. After a session has created a temporary table, the server performs no further privilege checks on the table. The creating session can perform any operation on the table, such as DROP TABLE , INSERT , UPDATE , or SELECT .
How do I select a temporary table in MySQL?
The general syntax would be like this: INSERT INTO temporary_tabel_name SELECT * FROM existing table_name; Following the general syntax, we will copy the data from the existing table, named, Guys into the newly created temporary table, named, “temporary_data”.
Example
The following program is an example showing you the usage of the temporary table. The same code can be used in PHP scripts using the mysql_query() function.
mysql> CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE SalesSummary (
-> product_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
-> , total_sales DECIMAL(12,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.00
-> , avg_unit_price DECIMAL(7,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.00
-> , total_units_sold INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0
);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO SalesSummary
-> (product_name, total_sales, avg_unit_price, total_units_sold)
-> VALUES
-> ('cucumber', 100.25, 90, 2);
mysql> SELECT * FROM SalesSummary;
+--------------+-------------+----------------+------------------+
| product_name | total_sales | avg_unit_price | total_units_sold |
+--------------+-------------+----------------+------------------+
| cucumber | 100.25 | 90.00 | 2 |
+--------------+-------------+----------------+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)When you issue a SHOW TABLES command, then your temporary table would not be listed out in the list. Now, if you will log out of the MySQL session and then you will issue a SELECT command, then you will find no data available in the database. Even your temporary table will not exist.
Dropping Temporary Tables
By default, all the temporary tables are deleted by MySQL when your database connection gets terminated. Still if you want to delete them in between, then you do so by issuing the DROP TABLE command.
The following program is an example on dropping a temporary table −
mysql> CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE SalesSummary (
-> product_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
-> , total_sales DECIMAL(12,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.00
-> , avg_unit_price DECIMAL(7,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.00
-> , total_units_sold INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0
);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO SalesSummary
-> (product_name, total_sales, avg_unit_price, total_units_sold)
-> VALUES
-> ('cucumber', 100.25, 90, 2);
mysql> SELECT * FROM SalesSummary;
+--------------+-------------+----------------+------------------+
| product_name | total_sales | avg_unit_price | total_units_sold |
+--------------+-------------+----------------+------------------+
| cucumber | 100.25 | 90.00 | 2 |
+--------------+-------------+----------------+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> DROP TABLE SalesSummary;
mysql> SELECT * FROM SalesSummary;
ERROR 1146: Table 'TUTORIALS.SalesSummary' doesn't existFeatures
A temporary table in MySQL has many features, which are given below:
- MySQL uses the CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE statement to create a temporary table.
- This statement can only be used when the MySQL server has the CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES privilege.
- It can be visible and accessible to the client who creates it, which means two different clients can use the temporary tables with the same name without conflicting with each other. It is because this table can only be seen by that client who creates it. Thus, the user cannot create two temporary tables with the same name in the same session.
- A temporary table in MySQL will be dropped automatically when the user closes the session or terminates the connection manually.
- A temporary table can be created by the user with the same name as a normal table in a database. For example, if the user creates a temporary table with the name student, then the existing student table cannot be accessible. So, the user performs any query against the student table, is now going to refer to the temporary student table. When the user removes a temporary table, the permanent student table becomes accessible again.
Syntax of Creating Temporary Table
In MySQL, the syntax of creating a temporary table is the same as the syntax of creating a normal table statement except the TEMPORARY keyword. Let us see the following statement which creates the temporary table:
- mysql> CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE table_name (
- column_1, column_2, …, table_constraints
- );
If the user wants to create a temporary table whose structure is the same as an existing table in the database, then the above statement cannot be used. Instead, we use the syntax as given below:
- Mysql> CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temporary_table_name SELECT * FROM original_table_name LIMIT 0;
MySQL Temporary Table Example
Let us understand how we can create a temporary table in MySQL. Execute the following statement that creates a temporary table in the selected database:
- mysql> CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE Students( student_name VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL, total_marks DECIMAL(12,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.00, total_subjects INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0);
We can see the below image:
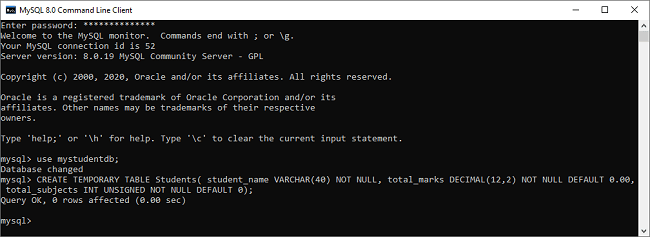
Next, we need to insert values in the temporary table:
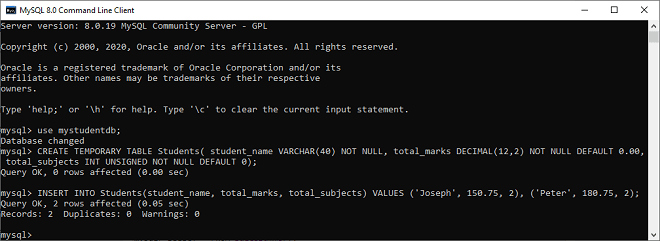
- mysql>INSERT INTO Students(student_name, total_marks, total_subjects) VALUES (‘Joseph’, 150.75, 2), (‘Peter’, 180.75, 2);
After executing the above statement, it will give the below output:
Now, run the following query to get the result:
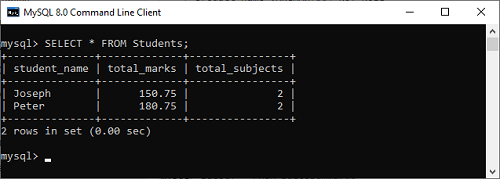
- mysql> SELECT * FROM Students;
After the successful execution of the above statement, we will get the output as below:
It is to be noted that when we run a SHOW TABLES command, then our temporary table will not be shown on the list. Also, if we close the current session and then will execute the SELECT statement, we will get a message saying that no data available in the database, and even the temporary table will not exist.
A Temporary Table whose structure is based on a normal table
In this example, we are going to create a temporary table whose structure is based on the already available tables in the database. Suppose our database has the following table as permanent:
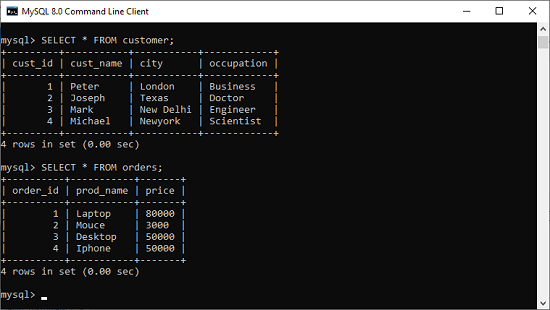
Here, the structure of a temporary table is created by using the SELECT statement and merge two tables using the INNER JOIN clause and sorts them based on the price. Write the following statement in the MySQL prompt:
- CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_customers
- SELECT c.cust_name, c.city, o.prod_name, o.price
- FROM orders o
- INNER JOIN customer c ON c.cust_id = o.order_id
- ORDER BY o.price DESC;
When we execute the above statement, we will get the following message:
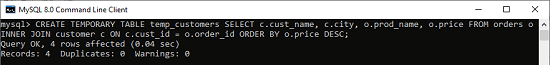
Now, run the below command to see the temporary table:
- mysql> SELECT * FROM temp_customers;
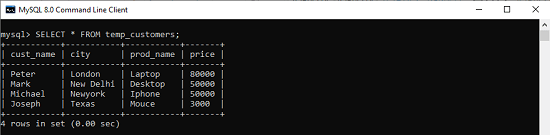
We can also perform queries from the above temporary table “temp_customers” similar to the querying data from a permanent table. The following query explains it more clearly:
- Mysql> SELECT cust_name, prod_name, price FROM temp_customers;
After executing the above statement, it will give the output as below:
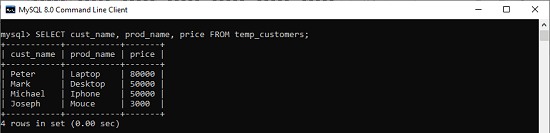
NOTE: It is noted that we can use IF NOT EXISTS keyword to avoid the “table already exists” error.
How to Drop Temporary Table in MySQL
MySQL allows us to remove the temporary table using the DROP TABLE statement. But, it”s a good practice to use the TEMPORARY keyword with the DROP TABLE statement. This keyword helps us to avoid the mistake of deleting a permanent table when the temporary table and permanent table have the same name in the current session. So, it is recommended to use the following query for removing the temporary table:
- mysql> DROP TEMPORARY TABLE table_name;
This query will not remove a permanent table of the database that means it only deletes a temporary table. If we try to delete a permanent table with this statement, it will throw an error message saying that you are deleting a table is unknown. For example, if we want to remove the above temporary table “temp_customers”, we need to use the following statements .
2. mysql> DROP TEMPORARY TABLE top_customers;


