If you are interested to learn about the Cyber attacks
In computer and computer networks, an attacker is the individual or organization who performs the malicious activities to destroy, expose, alter, disable, steal or gain unauthorized access to or make unauthorized use of an asset. As the Internet access becomes more pervasive across the world, and each of us spends more time on the web, there is also an attacker grows as well. Attackers use every tools and techniques they would try and attack us to get unauthorized access. There are four types of attackers which are described below-
Cyber Criminals
Cybercriminals are individual or group of people who use technology to commit cybercrime with the intention of stealing sensitive company information or personal data and generating profits. In today’s, they are the most prominent and most active type of attacker.
Cybercriminals use computers in three broad ways to do cybercrimes-
- Select computer as their target– In this, they attack other people’s computers to do cybercrime, such as spreading viruses, data theft, identity theft, etc.
- Uses the computer as their weapon– In this, they use the computer to do conventional crime such as spam, fraud, illegal gambling, etc.
- Uses the computer as their accessory– In this, they use the computer to steal data illegally.
Who are Cyber Attackers?
Cyber Attackers are malicious programmers who try to gain access to your system while you are connected to the internet.
Attackers employ several tools and methodologies to gain access to your system without you noticing it. They exploit your personal information on your compromised system. Depending on the motive of the attacker, they may demand a ransom or damage your data.
Cyber Attacker’s Motive
The motive behind cybercrimes is not the same for all types of attackers. While money and information gain is the prime motive behind the majority of the crimes, there are other reasons as well. Businesses have competitors around the globe and some firms may hire a contract-based hacker. The aim is to spoil the reputation or cause financial losses to fellow competitors. Some cybercriminals want to prove a political point or even manipulate elections. Some are thrill-seekers who just hack the system to enjoy being able to exploit a vulnerability.
Understanding the motive behind cyber-attacks helps us to determine what to protect from them.
Evolution of Cyber Attackers
The increase in sophistication of the attackers grew along with the internet itself. The birth of the first cyberattack was with the invention of the computer worm. It traveled on the internet, leaving a trail and a message. It was not an attack but an academic prank.
Gradually the notions of the attackers started to phase towards illicit gains. The below diagram briefs about the 5 generations of cyber attackers.
Hacktivists
Hacktivists are individuals or groups of hackers who carry out malicious activity to promote a political agenda, religious belief, or social ideology. According to Dan Lohrmann, chief security officer for Security Mentor, a national security training firm that works with states said “Hacktivism is a digital disobedience. It’s hacking for a cause.” Hacktivists are not like cybercriminals who hack computer networks to steal data for the cash. They are individuals or groups of hackers who work together and see themselves as fighting injustice.
State-sponsored Attacker
State-sponsored attackers have particular objectives aligned with either the political, commercial or military interests of their country of origin. These type of attackers are not in a hurry. The government organizations have highly skilled hackers and specialize in detecting vulnerabilities and exploiting these before the holes are patched. It is very challenging to defeat these attackers due to the vast resources at their disposal.
Insider Threats
The insider threat is a threat to an organization’s security or data that comes from within. These type of threats are usually occurred from employees or former employees, but may also arise from third parties, including contractors, temporary workers, employees or customers.
Insider threats can be categorized below-
Malicious-
Malicious threats are attempts by an insider to access and potentially harm an organization’s data, systems or IT infrastructure. These insider threats are often attributed to dissatisfied employees or ex-employees who believe that the organization was doing something wrong with them in some way, and they feel justified in seeking revenge. Insiders may also become threats when they are disguised by malicious outsiders, either through financial incentives or extortion.
Accidental-
Accidental threats are threats which are accidently done by insider employees. In this type of threats, an employee might accidentally delete an important file or inadvertently share confidential data with a business partner going beyond company?s policy or legal requirements.
Negligent-
These are the threats in which employees try to avoid the policies of an organization put in place to protect endpoints and valuable data. For example, if the organization have strict policies for external file sharing, employees might try to share work on public cloud applications so that they can work at home. There is nothing wrong with these acts, but they can open up to dangerous threats nonetheless.
Types of Cyber Attackers
Cyber attackers present themselves in different forms based on their motivation and methodology of attack. They can be broadly classified into the following types:
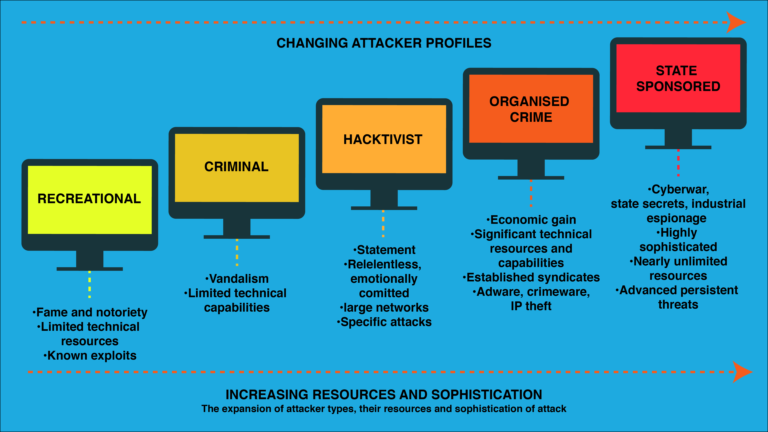
1. Recreational Cyber Attackers
The main motive behind these types of attackers is fame and notoriety. They have limited resources and know which vulnerability to exploit for their cause.
2. Script kiddies Cyber Attackers
These are amateurs who learn from the internet and use available tools to crack a system. These noobs are harmless with less skill and do not cause heavy damage to the system. They enjoy being challenged and seek the thrill from it. Over time they may gain experience and even become professional hackers.
3. Cyber Criminals Cyber Attackers
These attackers constitute an individual or a group of individuals whose aim is to exploit sensitive information of the user. They either capture the system and the data for financial gains. They undertake various approaches to achieve their purpose. Some of them are spreading viruses in a system, spamming the user with infected messages, or even stealing sensitive information of the user or a business.
4. Hacktivists Cyber Attackers
Hacktivists are those who perform malicious and fraudulent tasks to promote a political agenda. Hacktivism is a digital disobedience undertaken for a cause. Hacktivists fight for justice and do not go behind financial gains. Sometimes they pair up with malicious insiders to expose sensitive data.
5. State-sponsored Cyber Attackers
State-sponsored attackers have specific goals associating with either the political or military origin of their country. They use unlimited resources and highly sophisticated technologies. They often cause advanced persistent threats. Cyberwars, industrial espionage, and leaking state secrets are some of the attacks done by state-sponsored attackers.
6. Insider threats Cyber Attackers
Insiders come from within an organization and pose a threat to the security of valuable data the company holds. When the needs of the employee are dissatisfied they become disgruntled employees and eventually hackers.
The insiders threaten the safety of the internal systems. These insiders may be financially motivated and some may even be unintentional. Former employees, temporary workers, or even customers may play the role of an insider.
Insider threats are of the following types:
a. Malicious Insider Threats
Malicious insiders steal the company’s data and cause damage to the system infrastructure. Dissatisfied employees turn into malicious insiders to seek revenge against the organization.
b. Accidental Insider Threats
These are unintentional damages done to the company by its employees. Accidental deletion or modification of important files is an example of an accidental insider.
c. Negligent Insider Threats
These occur due to the carelessness of an employee. This happens when an employee fails to follow the policies and procedures framed by an organization. The policies are put in place to protect the integrity of data and when not followed might accumulate to end up in a huge loss open vulnerability for threats.
7. Organized Crime Cyber Attackers
These occur due to the carelessness of an employee. This happens when an employee fails to follow the policies and procedures framed by an organization. The policies are put in place to protect the integrity of data and when not followed might accumulate to end up in a huge loss open vulnerability for threats.
8. Hackers
Hackers possess the technical skills to breach the data by exploiting any vulnerability in the system or network. They have the skills to gain unauthorized access to your system.Hackers classified into 3 types based on their intent:
a. White hat hackers
These hackers use their skills in a just and lawful manner to determine the loose ends of the security of an organization. To boost the protection of the system and identify the weakness of the network, organizations hire white hat hackers.
b. Gray hat Hackers
These hackers crack through the security of an organization only to inform them later about it. They do not cause any harm but simply disclose the weakness in the security of the compromised network.
c. Black hat Hackers
They are unethical hackers who hack the system and networks and misuse it for personal benefits.
9. Nation-State Actors or Cyberterrorists
These attackers work in favor of the government and other vital businesses that run critical infrastructures for the society like power grids. They aim to steal highly sensitive information, damage opponent’s facilities, or launch an international incident. They work directly or indirectly for the government employing sophisticated attacking techniques against enemies. These attackers are patriots and work to put the nation in a better position by causing high-intensity damages to enemies.
Cyber Attackers Actions
The actions performed by the attackers give us a better insight into the motivation behind it. Cyber attackers are classified into 3 types based on their actions:
1. Inadvertent Cyber Attackers
These kinds of actions are generally done by the insiders and are done without any harmful intent.
2. Deliberate Cyber Attackers
These actions have a negative intent to cause damage to an individual or an organization. They may be an insider or an outsider.
The 3 major motives behind deliberate actions are:
a. Political motivation – like protest, making political statements.
b. Economic motivation – theft of intellectual property, blackmail.
c. Socio-Cultural motivation – publicity, ego gratification.
3. Inaction
This occurs when a person failed to act in a certain situation, compromising security.
How to deceive Cyber Attackers and protect yourself
- Conceal valuable data in innocuous files to distract the attacker.
- Camouflage your infrastructure by changing the address and topologies regularly.
- Confuse the attacker with false information like fake assets to exploit.
- Gain actionable insights from your cybersecurity advisory.
- Make use of technologies like intrusion prevention systems and firewalls to safeguard the information.
Summary
Cyber attackers are malicious attackers who breach the security of the user and exploit the data. The motivation behind the attack varies from person to person. Their advancement in technology has increased the sophistication of cyber attacks in recent years.
Based on the methodologies, target, and intent, cyber attackers are of various types. There are several tools available in cybersecurity to protect ourselves from theft and sabotage.


