If you are interested to learn about the Cyber Security
Driven by Money
There are a few key threats organizations face frequently:
- Ransomware files and systems are encrypted with attackers keys and they demand you to pay money to get your data back.
- Cryptocurrency miners; your systems are infected with a low-profile cryptocurrency mining tool. This tool uses the CPU to try make money on a cryptocurrency for the attackers.
- BEC (“Business Email Compromise”). Users get hacked through all sorts of methods and their emails are compromised. Via email compromise the attackers can intercept communications, for example an invoice, and try to redirect payments to other banks and accounts.
There are plenty of ways of making money for cyber criminals, which attracts people and interest.
Value and Power
There is value and power in many things related to IT, for example:
- Bandwidth can be used to pressure businesses by targeting them with DDOS (“Distributed Denial of Service”) attacks.
- Hacked systems may have sensitive information worth money, for example business proprietary information, online gaming assets, sensitive photographs and pictures.
- Attackers can install themselves in browsers and try to hijack the online banking use.
The potential for criminals to make significant amounts of money within the cyber domain causes more and more criminal gangs and other opportunists to join in on the action and make our lives much harder.
Threatening for Money
Another common attack cyber criminals perform to make money is the act of extortion, that is holding individuals hostage based on information they have on a individual, trying to make them pay money to be released from the extortion attempt. Consider the following common scenario:
- A person meets up with someone online, the other party is actually a scam artists trying to trick the victim.
- They engage in interesting conversations and seem to make an immediate deep bond between one another.
- They might even engage in video conversations, but the scam artists is for example using recorded video or simply has an excuse for not being able to activate their microphone or web-camera.
- One thing might lead to another and the relationship could turn sexual. The scam artist tries to convince the victim in giving up personal pictures and recordings of themselves, likely in compromising situations.
- Once the scam artist receives this material, perhaps even returning fake pictures of innocent people in similar situations, the extortion begins.
- The scam artist can now threaten to release the compromising material to family members, co-workers and others, offering to delete the material if a sum of money is paid into the scam artists account.
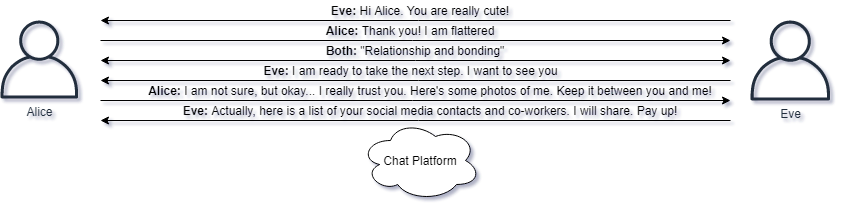
Stories like these are far from uncommon, and there exists countless of different scenarios and opportunities for criminals to benefit from victims using the Internet without knowing the risks associated.
7 Types of Cyber Security Threats
Cyber security professionals should have an in-depth understanding of the following types of cyber security threats.
1. Malware
Malware is malicious software such as spyware, ransomware, viruses and worms. Malware is activated when a user clicks on a malicious link or attachment, which leads to installing dangerous software. Cisco reports that malware, once activated, can:
- Block access to key network components (ransomware)
- Install additional harmful software
- Covertly obtain information by transmitting data from the hard drive (spyware)
- Disrupt individual parts, making the system inoperable
2. Emotet
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) describes Emotet as “an advanced, modular banking Trojan that primarily functions as a downloader or dropper of other banking Trojans. Emotet continues to be among the most costly and destructive malware.”
3. Denial of Service
A denial of service (DoS) is a type of cyber attack that floods a computer or network so it can’t respond to requests. A distributed DoS (DDoS) does the same thing, but the attack originates from a computer network. Cyber attackers often use a flood attack to disrupt the “handshake” process and carry out a DoS. Several other techniques may be used, and some cyber attackers use the time that a network is disabled to launch other attacks. A botnet is a type of DDoS in which millions of systems can be infected with malware and controlled by a hacker, according to Jeff Melnick of Netwrix, an information technology security software company. Botnets, sometimes called zombie systems, target and overwhelm a target’s processing capabilities. Botnets are in different geographic locations and hard to trace.
4. Man in the Middle
A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack occurs when hackers insert themselves into a two-party transaction. After interrupting the traffic, they can filter and steal data, according to Cisco. MITM attacks often occur when a visitor uses an unsecured public Wi-Fi network. Attackers insert themselves between the visitor and the network, and then use malware to install software and use data maliciously.
5. Phishing
Phishing attacks use fake communication, such as an email, to trick the receiver into opening it and carrying out the instructions inside, such as providing a credit card number. “The goal is to steal sensitive data like credit card and login information or to install malware on the victim’s machine,” Cisco reports.
6. SQL Injection
A Structured Query Language (SQL) injection is a type of cyber attack that results from inserting malicious code into a server that uses SQL. When infected, the server releases information. Submitting the malicious code can be as simple as entering it into a vulnerable website search box.
7. Password Attacks
With the right password, a cyber attacker has access to a wealth of information. Social engineering is a type of password attack that Data Insider defines as “a strategy cyber attackers use that relies heavily on human interaction and often involves tricking people into breaking standard security practices.” Other types of password attacks include accessing a password database or outright guessing.
Evolution of Cyber Security
Cyber security practices continue to evolve as the internet and digitally dependent operations develop and change. According to Secureworks, people who study cyber security are turning more of their attention to the two areas in the following sections.
The Internet of Things
Individual devices that connect to the internet or other networks offer an access point for hackers. Cytelligence reports that in 2019, hackers increasingly targeted smart home and internet of things (IoT) devices, such as smart TVs, voice assistants, connected baby monitors and cellphones. Hackers who successfully compromise a connected home not only gain access to users’ Wi-Fi credentials, but may also gain access to their data, such as medical records, bank statements and website login information.
The Explosion of Data
Data storage on devices such as laptops and cellphones makes it easier for cyber attackers to find an entry point into a network through a personal device. For example, in the May 2019 book Exploding Data: Reclaiming Our Cyber Security in the Digital Age, former U.S. Secretary of Homeland Security Michael Chertoff warns of a pervasive exposure of individuals’ personal information, which has become increasingly vulnerable to cyber attacks.
Consequently, companies and government agencies need maximum cyber security to protect their data and operations. Understanding how to address the latest evolving cyber threats is essential for cyber security professionals.


