The GROUP BY statement groups rows that have the same values into summary rows, like “find the number of customers in each country”. The GROUP BY statement is often used with aggregate functions (COUNT(), MAX(), MIN(), SUM(), AVG()) to group the result-set by one or more columns.
GROUP BY Syntax
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
GROUP BY column_name(s)
ORDER BY column_name(s);Demo Database
Below is a selection from the “Customers” table in the Northwind sample database:
| CustomerID | CustomerName | ContactName | Address | City | PostalCode | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alfreds Futterkiste | Maria Anders | Obere Str. 57 | Berlin | 12209 | Germany |
| 2 | Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados | Ana Trujillo | Avda. de la Constitución 2222 | México D.F. | 05021 | Mexico |
| 3 | Antonio Moreno Taquería | Antonio Moreno | Mataderos 2312 | México D.F. | 05023 | Mexico |
| 4 | Around the Horn | Thomas Hardy | 120 Hanover Sq. | London | WA1 1DP | UK |
| 5 | Berglunds snabbköp | Christina Berglund | Berguvsvägen 8 | Luleå | S-958 22 | Sweden |
MySQL GROUP BY Examples
The following SQL statement lists the number of customers in each country:
Example
SELECT COUNT(CustomerID), Country<br>FROM Customers<br>GROUP BY Country;
The following SQL statement lists the number of customers in each country, sorted high to low:
Example
SELECT COUNT(CustomerID), Country<br>FROM Customers<br>GROUP BY Country<br>ORDER BY COUNT(CustomerID) DESC;
Demo Database
Below is a selection from the “Orders” table in the Northwind sample database:
| OrderID | CustomerID | EmployeeID | OrderDate | ShipperID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10248 | 90 | 5 | 1996-07-04 | 3 |
| 10249 | 81 | 6 | 1996-07-05 | 1 |
| 10250 | 34 | 4 | 1996-07-08 | 2 |
And a selection from the “Shippers” table:
| ShipperID | ShipperName |
|---|---|
| 1 | Speedy Express |
| 2 | United Package |
| 3 | Federal Shipping |
GROUP BY With JOIN Example
The following SQL statement lists the number of orders sent by each shipper:
Example
SELECT Shippers.ShipperName, COUNT(Orders.OrderID) AS NumberOfOrders FROM Orders<br>LEFT JOIN Shippers ON Orders.ShipperID = Shippers.ShipperID<br>GROUP BY ShipperName;
MySQL GROUP BY Clause
The MYSQL GROUP BY Clause is used to collect data from multiple records and group the result by one or more column. It is generally used in a SELECT statement.
You can also use some aggregate functions like COUNT, SUM, MIN, MAX, AVG etc. on the grouped column.
Syntax:
SELECT expression1, expression2, ... expression_n,
aggregate_function (expression)
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions]
GROUP BY expression1, expression2, ... expression_n; Parameters
aggregate_function: It specifies a function such as SUM, COUNT, MIN, MAX, or AVG etc. tables: It specifies the tables, from where you want to retrieve the records. There must be at least one table listed in the FROM clause.
WHERE conditions: It is optional. It specifies the conditions that must be fulfilled for the records to be selected.
(i) MySQL GROUP BY Clause with COUNT function
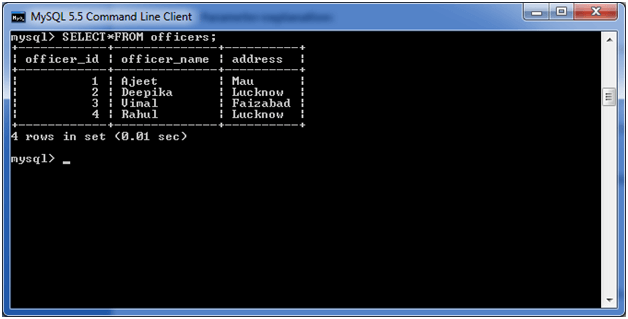
Consider a table named “officers” table, having the following records.
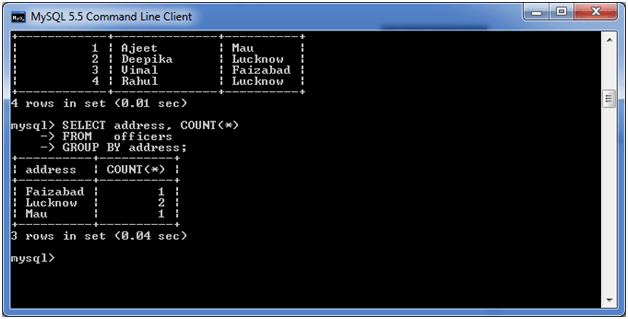
Now, let’s count repetitive number of cities in the column address.
Execute the following query:
SELECT address, COUNT(*) FROM officers GROUP BY address;
Output:
(ii) MySQL GROUP BY Clause with SUM function
Let’s take a table “employees” table, having the following data.
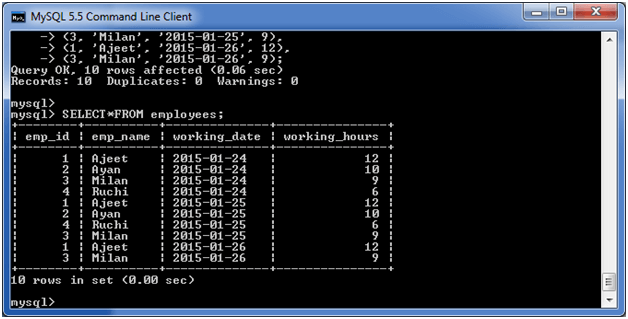
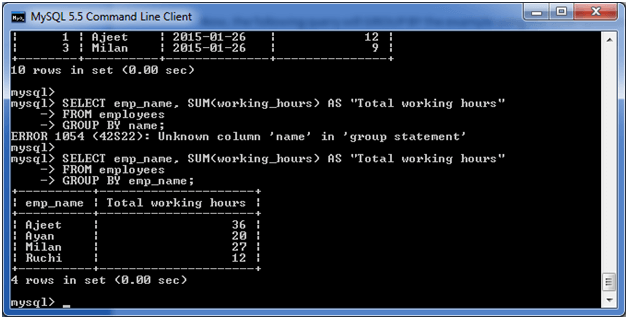
Now, the following query will GROUP BY the example using the SUM function and return the emp_name and total working hours of each employee.
Execute the following query:
SELECT emp_name, SUM(working_hours) AS "Total working hours" FROM employees GROUP BY emp_name;
Output:
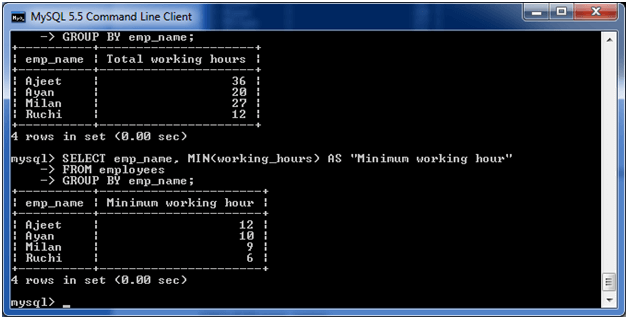
(iii) MySQL GROUP BY Clause with MIN function
The following example specifies the minimum working hours of the employees form the table “employees”.
Execute the following query:
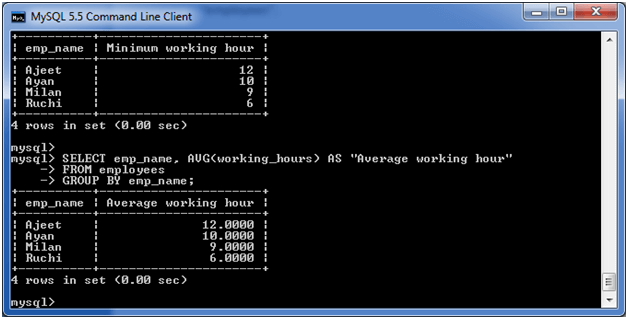
SELECT emp_name, MIN(working_hours) AS "Minimum working hour" FROM employees GROUP BY emp_name;
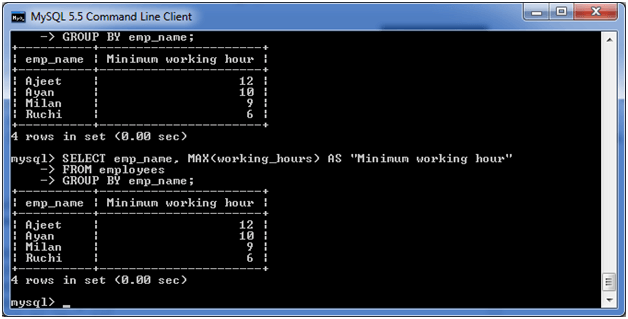
(iv) MySQL GROUP BY Clause with MAX function
The following example specifies the maximum working hours of the employees form the table “employees”.
Execute the following query:
SELECT emp_name, MAX (working_hours) AS "Minimum working hour" FROM employees GROUP BY emp_name;
Output:
(v) MySQL GROUP BY Clause with AVG function
The following example specifies the average working hours of the employees form the table “employees”.
Execute the following query:
<strong>SELECT</strong> emp_name, AVG(working_hours) <strong>AS</strong> "Average working hour"
FROM employees
GROUP BY emp_name;
Output:
: