If you are interested to learn about the python – networking program
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a protocol, which handles sending e-mail and routing e-mail between mail servers. Python provides smtplib module, which defines an SMTP client session object that can be used to send mail to any Internet machine with an SMTP or ESMTP listener daemon. Here is a simple syntax to create one SMTP object, which can later be used to send an e-mail −
import smtplib
smtpObj = smtplib.SMTP( [host [, port [, local_hostname]]] )Here is the detail of the parameters −
- host − This is the host running your SMTP server. You can specify IP address of the host or a domain name like tutorialspoint.com. This is optional argument.
- port − If you are providing host argument, then you need to specify a port, where SMTP server is listening. Usually this port would be 25.
- local_hostname − If your SMTP server is running on your local machine, then you can specify just localhost as of this option.
An SMTP object has an instance method called sendmail, which is typically used to do the work of mailing a message. It takes three parameters −
- The sender − A string with the address of the sender.
- The receivers − A list of strings, one for each recipient.
- The message − A message as a string formatted as specified in the various RFCs.
Example
Here is a simple way to send one e-mail using Python script. Try it once −
#!/usr/bin/python
import smtplib
sender = 'from@fromdomain.com'
receivers = ['to@todomain.com']
message = """From: From Person <from@fromdomain.com>
To: To Person <to@todomain.com>
Subject: SMTP e-mail test
This is a test e-mail message.
"""
try:
smtpObj = smtplib.SMTP('localhost')
smtpObj.sendmail(sender, receivers, message)
print "Successfully sent email"
except SMTPException:
print "Error: unable to send email"Here, you have placed a basic e-mail in message, using a triple quote, taking care to format the headers correctly. An e-mail requires a From, To, and Subject header, separated from the body of the e-mail with a blank line.
To send the mail you use smtpObj to connect to the SMTP server on the local machine and then use the sendmail method along with the message, the from address, and the destination address as parameters (even though the from and to addresses are within the e-mail itself, these aren’t always used to route mail). If you are not running an SMTP server on your local machine, you can use smtplib client to communicate with a remote SMTP server. Unless you are using a webmail service (such as Hotmail or Yahoo! Mail), your e-mail provider must have provided you with outgoing mail server details that you can supply them, as follows −
smtplib.SMTP('mail.your-domain.com', 25)
Sending an HTML e-mail using Python
When you send a text message using Python, then all the content are treated as simple text. Even if you include HTML tags in a text message, it is displayed as simple text and HTML tags will not be formatted according to HTML syntax. But Python provides option to send an HTML message as actual HTML message. While sending an e-mail message, you can specify a Mime version, content type and character set to send an HTML e-mail.
Example
Following is the example to send HTML content as an e-mail. Try it once −
#!/usr/bin/python
import smtplib
message = """From: From Person <from@fromdomain.com>
To: To Person <to@todomain.com>
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-type: text/html
Subject: SMTP HTML e-mail test
This is an e-mail message to be sent in HTML format
<b>This is HTML message.</b>
<h1>This is headline.</h1>
"""
try:
smtpObj = smtplib.SMTP('localhost')
smtpObj.sendmail(sender, receivers, message)
print "Successfully sent email"
except SMTPException:
print "Error: unable to send email"Sending Attachments as an E-mail
To send an e-mail with mixed content requires to set Content-type header to multipart/mixed. Then, text and attachment sections can be specified within boundaries. A boundary is started with two hyphens followed by a unique number, which cannot appear in the message part of the e-mail. A final boundary denoting the e-mail’s final section must also end with two hyphens. Attached files should be encoded with the pack(“m”) function to have base64 encoding before transmission.
Example
Following is the example, which sends a file /tmp/test.txt as an attachment. Try it once −
#!/usr/bin/python
import smtplib
import base64
filename = "/tmp/test.txt"
# Read a file and encode it into base64 format
fo = open(filename, "rb")
filecontent = fo.read()
encodedcontent = base64.b64encode(filecontent) # base64
sender = 'webmaster@tutorialpoint.com'
reciever = 'amrood.admin@gmail.com'
marker = "AUNIQUEMARKER"
body ="""
This is a test email to send an attachement.
"""
# Define the main headers.
part1 = """From: From Person <me@fromdomain.net>
To: To Person <amrood.admin@gmail.com>
Subject: Sending Attachement
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: multipart/mixed; boundary=%s
--%s
""" % (marker, marker)
# Define the message action
part2 = """Content-Type: text/plain
Content-Transfer-Encoding:8bit
%s
--%s
""" % (body,marker)
# Define the attachment section
part3 = """Content-Type: multipart/mixed; name=\"%s\"
Content-Transfer-Encoding:base64
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename=%s
%s
--%s--
""" %(filename, filename, encodedcontent, marker)
message = part1 + part2 + part3
try:
smtpObj = smtplib.SMTP('localhost')
smtpObj.sendmail(sender, reciever, message)
print "Successfully sent email"
except Exception:
print "Error: unable to send email"
SMTP Authentication
STMP Authentication requires login to the SMTP Server. It has the following syntax –
SMTP.login(username, password)
The arguments are the username and password to authenticate with the server.
Start TLS
We should start the TLS for a security reason. It will encrypt all the commands following this.
starttls()
Send Mail
The sendmail() function is used to send mail to the recipients. It has the following syntax –
sendmail(from, to, msg)
Here, the from is the sender mail address and the to is the recipient mail address, the msg contains messages to be sent in the string.
Python Send Email Via SMTP | SMTP Server
Free Python course with 35 real-time projects Start Now!!
1. Objective
In this tutorial of Python Programming Language, we will learn how Python send Email via SMTP Server. Moreover, we will look at Python SMTP Server. Along with this, we will also discuss the working of SMTP server for sending a mail in Python. Also, we will look at Python send Email example. We will use the Python module smtplib for this. At last, we are going to discuss how Python send HTML Email using SMTP. So, let’s discuss the process of sending mail in Python via SMTP.
Sending Mail with Python 3 via SMTP
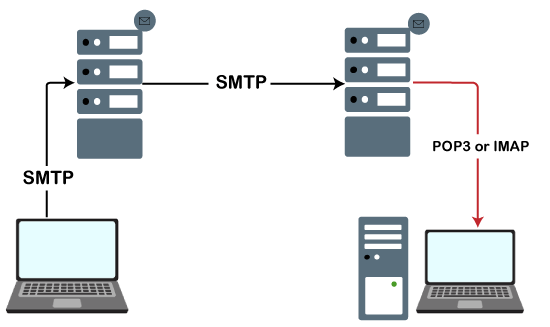
2. What is SMTP Server?
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is an application layer protocol in the OSI model. It lets a user send mail to another. Since this is a push protocol, we can use it to send a mail. At the receiver, this mail is retrieved using protocols POP (Post Office Protocol) and IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol).
Python Send Email- SMTP Serve
We need to start a server that is always listening for a request. As a client, we open a TCP connection to this server and then send the mail. When the server listens for a TCP connection from a client, it initiates a connection on port 587.
Have a look at Python Packages Comprehensive Guide
3. Python Send Email Using smtplib Module
We’ll use the smtplib module for sending Python Email. This is our Python SMTP script to send mail:
>>> import smtplib>>> sender='thesender@gmail.com'>>>
receiver='whicheverreceiver@gmail.com'>>> password=’<put your password here>'>>> smtpserver=smtplib.SMTP("smtp.gmail.com",587)>>> smtpserver.ehlo()
>>> smtpserver.starttls()>>> smtpserver.ehlo>>> smtpserver.login(sender,password)>>> msg='Subject:Demo\nThis is a demo>>> smtpserver.sendmail(sender,receiver,msg)>>> print('Sent')>>> smtpserver.close()4. How Does SMTP Work?
First, we import smtplib.
>>> import smtplib
Then, we set three strings- the sender’s and receiver’s email addresses and the sender’s password. Put your password for your mail ID in the string for a password.
>>> sender='thesender@gmail.com'>>> receiver='whicheverreceiver@gmail.com'>>> password=’<put your password here>'
Then, we create a server object using smptlib.SMTP(). We use the port 587 here, and the domain smtp.gmail.com.
>>> smtpserver=smtplib.SMTP("smtp.gmail.com",587)On this, we call the ehlo() method for Extended Hello. This lets the server identify the client, and also tells it that it must use the ESMTP (Extended SMTP) Protocol.
Read Python Datetime Module with Quick Examples
>>> smtpserver.ehlo()
Then, we call starttls() to use a transport layer security connection.
>>> smtpserver.starttls()
And then we call ehlo() again.
>>> smtpserver.ehlo
Then, we call the login() method on this server object. To this, we pass the parameters sender and password to let the client gain access from the Gmail server to send a mail.
>>> smtpserver.login(sender,password)
Then, we decide the message to send. To set the subject for the message, we do:
>>> msg='Subject:Demo\nThis is a demo'
Now, we call the method sendmail() to send the mail in Python. To this, we pass sender, receiver, and msg.
.html>>> smtpserver .sendmail(sender,receiver,msg)
Finally, we print a success receipt to the client and then exit.
>>> print('Sent')>>> smtpserver.close()5. How to Send HTML Email in Python?
For sending an HTML Email you can also configure your message to be able to embed simple HTML code in it.
Import smtplib
>>> sender='thesender@gmail.com'>>> receiver=’whicheverreceiver@gmail.com'>>>
password='<your password>'>>> smtpserver=smtplib.SMTP("smtp.gmail.com",587)>>>
smtpserver.ehlo()>>> smtpserver.starttls()>>> smtpserver.ehlo>>> smtpserver.login
(sender,password)>>> msg="""From: AyushiTo: RuchiMIME-Version: 1.0Content-type: text/htmlSubject:DemoThis is a demo<br/><p align="center">Hi</p><hr/>""">>> smtpserver.sendmail(sender,receiver,msg)>>> print('Sent')>>> smtpserver.close()So, this was all about Python send Email using SMTP server. Hope you like our explanation.


